What is ambulatory blood pressure monitoring?
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) is a diagnostic procedure that measures blood pressure throughout everyday activities for 24 hours to determine the prevalence of hypertension. It aids in both the diagnosis of high blood pressure, which is typically characterized by a systolic pressure of atleast 140 mm Hg, and a diastolic pressure of at least 90 mm Hg.
Why is ABPM performed?
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is done for many purposes:
- This test takes multiple readings, as opposed to one or two during a typical clinic visit, so that the changes in blood pressure that occur naturally are replicated.
- The "white coat effect" occurs when a doctor takes blood pressure measures in a clinic, and those values are typically 9/7 mm Hg (systolic/diastolic pressure) higher than equivalent readings recorded by a nurse or other qualified practitioner in the same environment, is eliminated.
- It can identify both masked and prolonged hypertension. Masked hypertension is when the blood pressure reading is normal in the clinic but high during typical activities. Sustained hypertension is when the blood pressure remains high and is linked to an increased risk of heart strokes and kidney damage.
- It demonstrates the effects of current drugs, i.e., how they affect managing blood pressure throughout the day.
- It displays if the blood pressure rises at night or when sleeping, a phenomenon that some people experience and which may require a change in their medical regimen.
- It produces the average blood pressure, heart rate, and a few other parameters on average.
- It aids in predicting the likelihood of a heart attack or stroke.
How is ABPM performed?
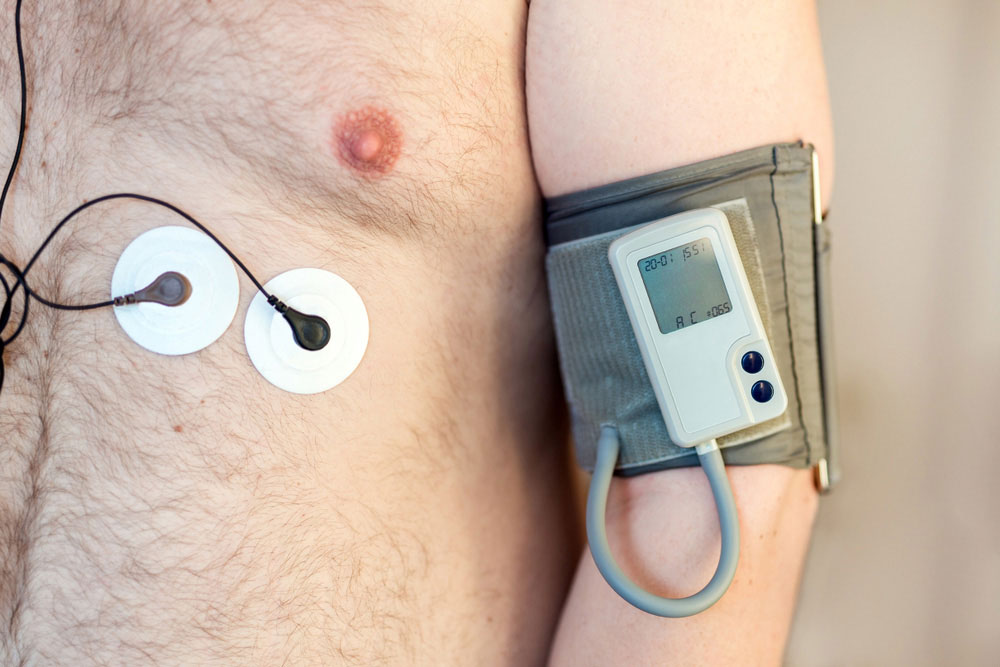
Continuous blood pressure readings are obtained for a full 24 hours. A device similar in size to a portable radio will be worn by you. The device is fastened to a belt or strap that you wear around your body. Throughout the 24-hour period, data is gathered and will subsequently be uploaded to a computer.
A BP cuff that is connected to the apparatus will be wrapped over your upper arm. (The cuff can be concealed by wearing garments.) At specific times during the day and night, the cuff inflates. You could be instructed to log your daily readings in a diary. This can demonstrate how variations in your blood pressure correspond to times of exercise or rest. You can remove the gadget after 24 hours.
What are the benefits of ABPM?
Ambulatory monitoring can rule out white-coat hypertension, preventing needless prescriptions for blood pressure-lowering medications. In order to make sure that patients receive the high blood pressure meds they require, it can also identify masked hypertension. In those people, the risk of stroke, heart disease, and organ damage brought on by hypertension can be decreased. Evaluation of a patient's reaction to long-acting antihypertensive medicines may also be possible by ambulatory monitoring.

 WhatsApp
WhatsApp